
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
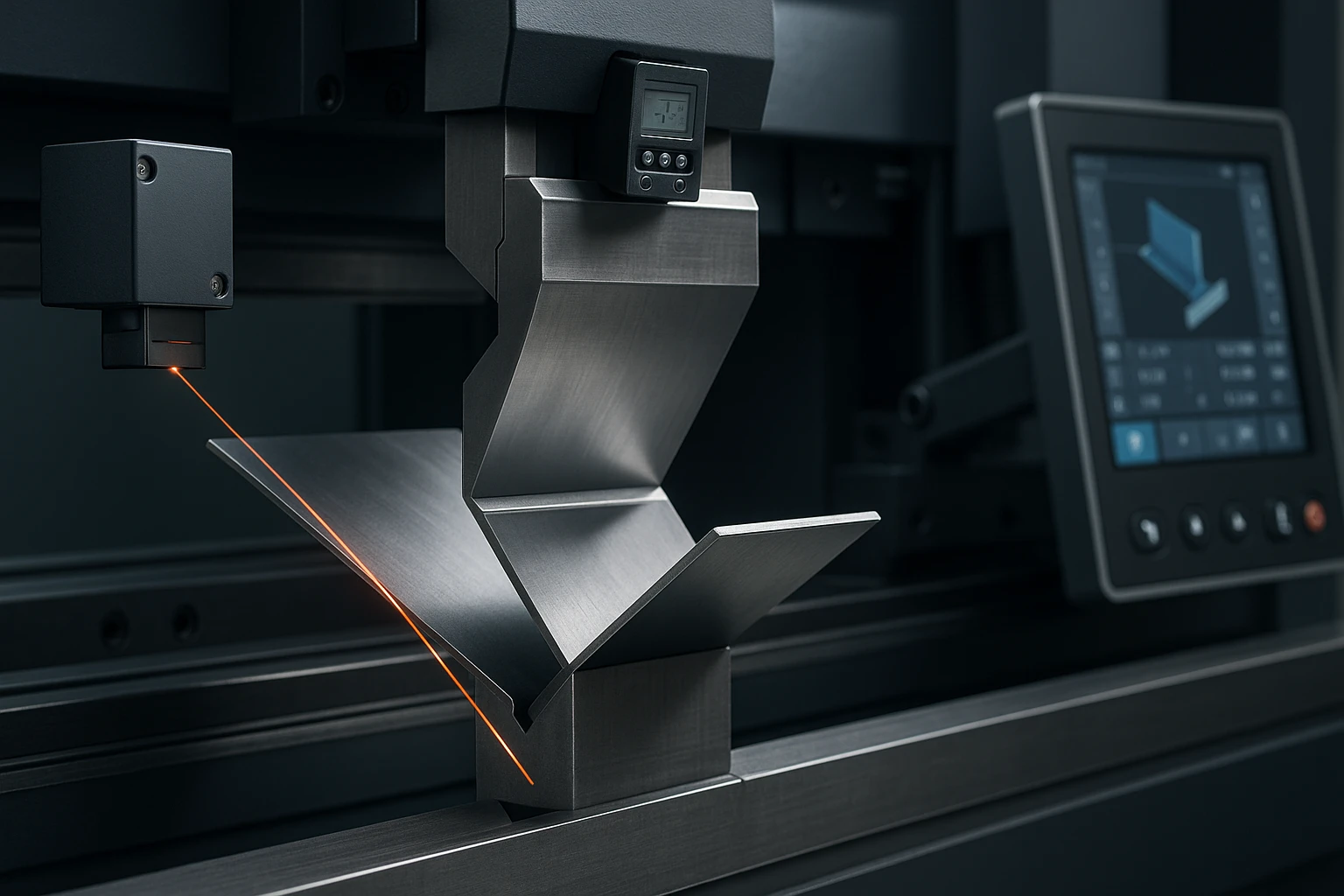
In the last decade, the global sheet-metal fabrication industry has undergone a profound transformation. As factories shift toward digital production and Industrie 4.0 standards, traditional press brake operations—once heavily dependent on manual skill—are now becoming automated, data-driven, and highly intelligent. The concept that best captures this transition is smart bending, a modern approach to sheet-metal bending powered by sensors, adaptive algorithms, and digitally connected workflows.
Smart bending does more than improve operator convenience. It reshapes the core of bending accuracy, cycle efficiency, and production consistency. Whether you are running a high-mix/low-volume factory, a large-scale OEM manufacturing line, or a job shop offering precision bending services, the adoption of smart bending technology directly influences competitiveness.
This article provides an in-depth explanation of what smart bending is, how it works, the technologies behind it, and why it is becoming the new backbone of intelligent press brake systems worldwide.
The term “smart bending” refers to an intelligent, automated bending process in which the press brake independently monitors, analyzes, and adjusts bending parameters in real time to guarantee accuracy and efficiency.
In traditional bending, the operator must manually set angles, backgauge positions, crowning, force levels, and sequence decisions. These steps require years of experience to achieve stable results.
Smart bending changes this fundamentally. It incorporates:
Instead of depending solely on operator intuition, the press brake becomes a self-optimizing machine.
Historically, bending accuracy has always been limited by three factors:
Manufacturers face increasing challenges:
To overcome these pressures, machine builders have been introducing features that measure, predict, and correct bending deviations before they cause defects. This is the essence of smart bending.
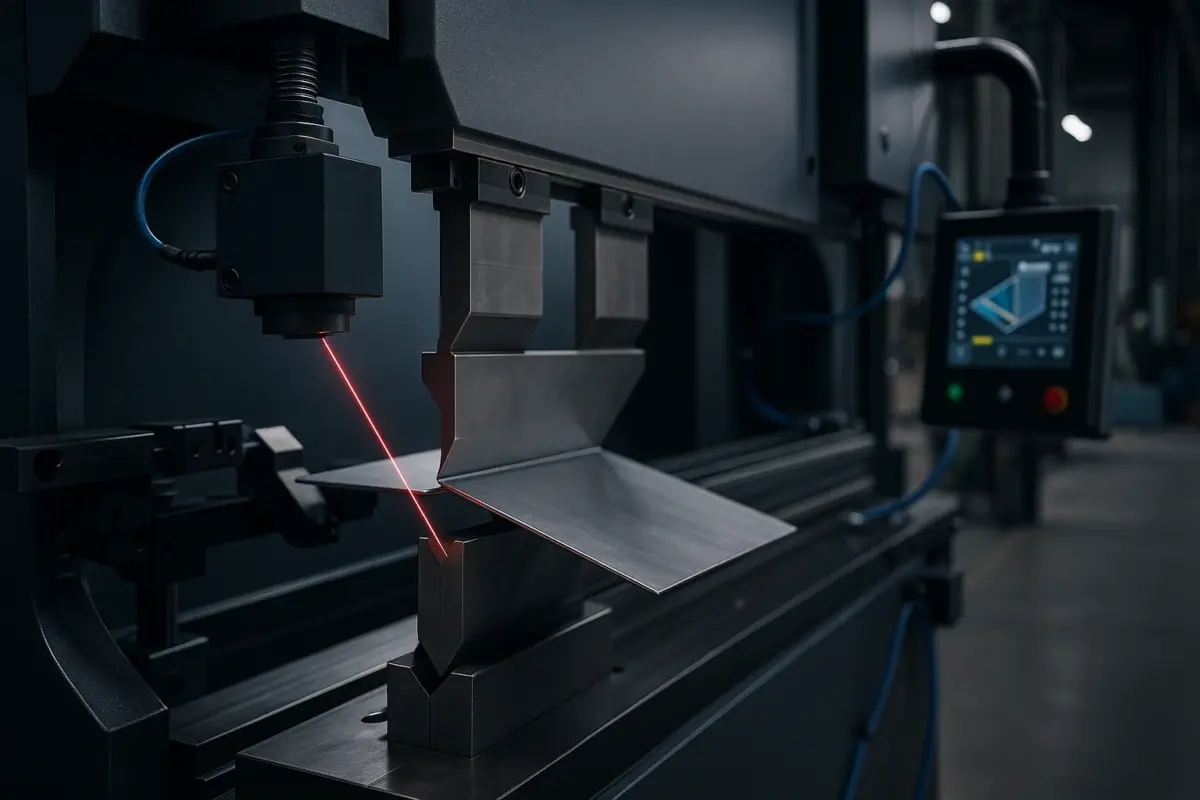

Smart bending is not a single feature but a combination of advanced technologies. These are the core building blocks that enable a press brake to think, analyze, and act autonomously.
Angle measurement is the most critical aspect of intelligent bending. Modern systems typically fall into two categories:
These tools physically contact the sheet and provide real-time angle feedback.
Non-contact sensors are more common in high-precision factories due to their speed and accuracy. Optical smart systems scan the sheet during forming and feed back the exact bend angle to the CNC controller.
The result: real-time error correction within milliseconds.
Smart bending systems automatically analyze machine deflection caused by:
A built-in algorithm adjusts crowning cylinders or mechanical wedges dynamically.
Unlike manual crowning based on charts or operator judgment, intelligent crowning compensates for:
This ensures that angles remain consistent from the first piece to the last, regardless of thickness or hardness variations.
A smart backgauge is more than an X-axis depth stop. It includes:
Smart bending integrates the backgauge with angle sensors and CNC data to:
The backgauge becomes part of the intelligence ecosystem, not just a positioning tool.
The CNC controller lies at the heart of smart bending. Modern systems store:
When the operator selects a material, the system predicts bending force, springback, and tonnage automatically.
True smart bending CNC software goes further:
This combination helps reduce human error and speeds up programming, achieving shorter lead times.
Artificial intelligence is now widely adopted in advanced press brakes. AI helps the system:
AI is particularly powerful in high-mix production, where every batch may involve different parts. As a smart bending system accumulates data, it becomes more accurate, efficient, and stable.
Modern factories rely on digital data. Smart bending systems support:
IoT connectivity transforms the press brake from a standalone machine into a data node within a smart factory.
Manufacturers can:
This significantly lowers downtime and enhances process reliability.
To understand the workflow, let’s walk through a typical smart bending cycle.
The operator imports a:
Or manually enters dimensions.
The CNC generates:
This eliminates much of the guesswork that traditional press brakes require.
Once the model is loaded, the CNC uses its internal database to calculate:
It suggests an optimal bending plan based on actual physics, historical data, and artificial intelligence.
During the first bend:
This continuous feedback loop allows an extremely tight angle tolerance—often ±0.3°, sometimes ±0.2° in premium systems.
If the angle differs from the target due to:
The CNC automatically modifies:
This occurs in real time and does not require manual intervention.
After several cycles, the machine optimizes itself:
This is what transforms traditional bending into smart bending.
Smart bending is not only about accuracy—it is fundamentally about productivity, consistency, and digital transformation.
Below are the most significant benefits.
A major challenge in the bending industry is the shortage of skilled operators. Smart bending allows factories to:
Experienced operators are still valuable, but the process becomes much less dependent on them.
Thanks to adaptive sensors and intelligent algorithms:
This helps reduce rework and scrap rates.
Smart bending systems automate:
This can reduce setup time from hours to minutes, especially in high-mix factories.
Smart bending optimizes:
It also reduces waiting time between operations. Over the long term, this provides substantial cost savings.
Smart bending naturally supports Industry 4.0 frameworks through:
It becomes a key element in digital manufacturing and modern smart factories.

Smart bending is particularly valuable in industries where accuracy, consistency, and part complexity are essential.
Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive OEMs require repeatability on large batch sizes—perfect for intelligent bending.
Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace bending benefits from adaptive sensing systems and material compensation algorithms.
HVAC and Ductwork
Smart bending simplifies work with thin materials, where springback is difficult to predict manually.
Electrical Cabinets and Enclosures
Box components often require dozens of bends, making automated sequence optimization extremely valuable.
Agricultural and Construction Machinery
Thick plates and high-strength steel demand precise tonnage prediction and sturdy crowning systems.
Furniture and Architecture
Complex angles and aesthetic accuracy make real-time angle measurement systems essential.
Although smart bending offers transformative benefits, it also presents challenges.
Smart bending systems require:
These increase machine cost, but usually provide a fast return on investment for high-mix or precision industries.
Optical systems must remain clean. Dirt, oil, and dust can:
Proper maintenance schedules are crucial.
Highly reflective, perforated, or textured materials can interfere with optical scanning systems. Some machines include special calibration modes to address this.
Smart bending is still evolving. Future innovations will include:
Full AI-operated press brakes
Machines that run autonomously, requiring only minimal human supervision.
Digital twins
Virtual copies of press brakes and bending processes, allowing remote optimization.
Self-programming machines
The operator simply uploads a drawing; the machine performs everything else automatically.
Robotic integration
Robots will handle loading, bending, flipping, and unloading with zero manual intervention.
Universal material behavior prediction
AI models will learn global material patterns, not just factory-specific data.
Smart bending is more than a technological upgrade—it represents a complete reinvention of how sheet-metal bending is performed. By integrating sensors, intelligent CNC control, AI-driven algorithms, and connected data systems, smart bending transforms the press brake from a manual-skill-dependent tool into a highly automated and intelligent production platform.
For manufacturers facing challenges such as labor shortages, tight tolerance requirements, and diverse material batches, smart bending provides a clear path toward higher productivity, stronger competitiveness, and long-term operational stability.
As the press brake industry continues its transition toward digitalization, smart bending will increasingly become the foundation of intelligent fabrication.